Ammonium Iodide E.P.
₹ 1,330.00 – ₹ 14,100.00Price range: ₹ 1,330.00 through ₹ 14,100.00
Product Specifications
CAS NO. 12027-06-4
HSN CODE : 28276090
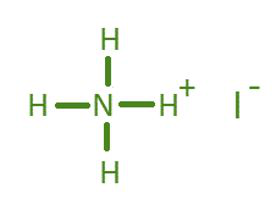
- Molecular Formula: NH₄I
- Molecular Weight: 144.94 g/mol
- Appearance: White, hygroscopic crystalline powder
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water and ethanol
- Melting Point: 551°C (decomposes)
- Stability: Stable under dry conditions but decomposes on exposure to light or moisture, releasing iodine.
HealthChemix Support
GST Invoice Available
Secure Payments
365 Days Help Desk
Return & Warranty Policy
Product Details
Ammonium Iodide E.P. / CAS NO. 12027-06-4
Ammonium iodide (NH₄I) is an inorganic compound that is the iodide salt of ammonia. It is a white crystalline substance with a variety of applications in pharmaceuticals, analytical chemistry, and industrial processes. The E.P. (European Pharmacopoeia) designation indicates that it meets the purity standards required for pharmaceutical use. The CAS Number 12027-06-4 uniquely identifies this compound.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Molecular Formula: NH₄I
- Molecular Weight: 144.94 g/mol
- Appearance: White, hygroscopic crystalline powder
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water and ethanol
- Melting Point: 551°C (decomposes)
- Stability: Stable under dry conditions but decomposes on exposure to light or moisture, releasing iodine.
Applications of Ammonium Iodide
1. Pharmaceutical Applications
Ammonium iodide is used in pharmaceutical formulations due to its iodine content, which plays an essential role in various physiological functions:
- Iodine Supplementation: It can be used in the treatment of iodine deficiency-related disorders, such as goiter and hypothyroidism.
- Expectorants: Ammonium iodide is a common ingredient in expectorant formulations to loosen mucus and aid in respiratory conditions like bronchitis and asthma.
2. Analytical Chemistry
Ammonium iodide is widely utilized in analytical chemistry:
- Reagent in Redox Reactions: It is used as a reducing agent in various laboratory processes.
- Chemical Analysis: Ammonium iodide is employed in the detection and quantification of certain compounds, such as heavy metals and alkaloids.
3. Photography
Historically, ammonium iodide played a role in traditional photographic processes, particularly in the preparation of photographic emulsions. It contributed to the formation of light-sensitive silver iodide.
4. Industrial Uses
- Organic Synthesis: Ammonium iodide is used as a catalyst or reactant in the synthesis of certain organic compounds, especially in reactions requiring iodine sources.
- Iodinated Compounds: It is employed in the production of iodinated chemicals, such as pharmaceuticals and dyes.
5. Research Applications
In research laboratories, ammonium iodide is used for:
- Halogenation Reactions: A source of iodine in organic synthesis.
- Material Science: Investigating its properties for potential applications in new technologies, including optics and semiconductors.
Toxicity and Hazards of Ammonium Iodide
Health Hazards
Although ammonium iodide is generally considered safe in controlled quantities, it poses potential health risks under certain conditions:
- Acute Exposure:
- Inhalation: Can cause respiratory irritation.
- Skin Contact: May lead to irritation or an allergic reaction in sensitive individuals.
- Eye Contact: Causes irritation and redness.
- Ingestion: Can result in nausea, vomiting, or gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Chronic Exposure:
Prolonged exposure to ammonium iodide can lead to symptoms of iodism, including:- Metallic taste
- Excessive salivation
- Acneiform eruptions on the skin
Environmental Hazards
Ammonium iodide decomposes in the environment, releasing iodine. Excess iodine in water or soil can harm aquatic life and disrupt ecosystems.
Safety Measures for Handling Ammonium Iodide
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
When handling ammonium iodide, always use:
- Gloves to prevent skin contact.
- Safety goggles to protect the eyes.
- Lab coats or protective clothing.
- A dust mask or respirator in areas where ammonium iodide dust may be present.
2. Engineering Controls
- Use in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to minimize inhalation risks.
- Avoid exposure to light and moisture to prevent decomposition and iodine release.
3. Safe Storage
- Store in a tightly sealed container, in a cool, dry place away from light.
- Keep away from incompatible materials such as strong acids and oxidizing agents.
4. First Aid Measures
- Inhalation: Move the affected individual to fresh air. Seek medical attention if symptoms persist.
- Skin Contact: Wash thoroughly with soap and water. Remove contaminated clothing.
- Eye Contact: Flush eyes with water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical advice if irritation continues.
- Ingestion: Do not induce vomiting. Rinse mouth and seek immediate medical assistance.
Disposal Guidelines
Ammonium iodide should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations. Avoid releasing it into the environment. Use a licensed waste disposal service for proper handling and disposal.
Conclusion
Ammonium iodide (CAS NO. 12027-06-4) is a versatile compound with applications ranging from pharmaceuticals to analytical chemistry and industrial processes. Its role as an iodine source makes it valuable in treating iodine deficiencies, organic synthesis, and chemical analysis. However, its hygroscopic nature and potential hazards require careful handling, storage, and disposal. By adhering to safety measures, this compound can be utilized effectively in various fields while minimizing risks to health and the environment.
Other Product
Related products
-
Activated Charcoal Powder ( Charcoad Activated )
₹ 440.00 – ₹ 3,670.00Price range: ₹ 440.00 through ₹ 3,670.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Acetophenone E.P. ( For Synthesis )
₹ 930.00 – ₹ 3,810.00Price range: ₹ 930.00 through ₹ 3,810.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page